When choosing a school, many families ask themselves what are the differences between the British and the Spanish education systems? This question is particularly relevant in a country like Spain, where both models coexist and there is a wide range of schools offering the British curriculum. Although both systems aim to support students’ academic and personal development, they differ significantly in structure, methodology, assessment and educational approach. Understanding these differences is key to making an informed decision aligned with each family’s needs and expectations.
What is the difference between the British education system and the Spanish education system?
Educational stages
One of the first differences between the British and Spanish education systems lies in the organisation of educational stages. The British system is structured progressively and clearly by age, beginning with Early Years, followed by Primary Education and Secondary Education, which culminates in official qualifications such as IGCSEs and A-Levels. These stages are designed to adapt to students’ developmental needs and allow for gradual specialisation in later years.
The Spanish education system, by contrast, is organised into Early Childhood Education, Primary Education, Compulsory Secondary Education (ESO) and Bachillerato. Compulsory education extends until the age of 16, and academic specialisation usually takes place mainly during the final two years of Bachillerato.
This structural difference means that the British system introduces academic decision-making earlier, while the Spanish system maintains a more uniform curriculum for a longer period.
Teaching methodology
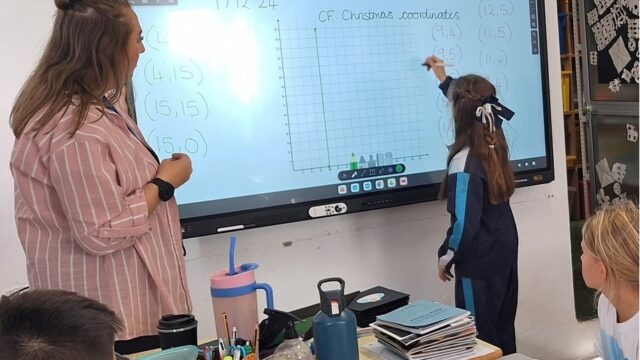
The pedagogical approach is one of the most notable differences between the two systems. The British education system is characterised by active, student-centred learning. Classroom participation, critical thinking, debate, research and the practical application of knowledge are strongly encouraged. Students play a central role in their own learning process, and their ability to reason, argue and solve problems is highly valued.
In the Spanish education system, although more participatory methodologies have been introduced in recent years, the traditional model has historically focused more on content delivery and theoretical learning. Teachers tend to have a more directive role, and students often adopt a more receptive position, particularly during compulsory education stages.
Assessment system and student monitoring
Assessment is another key area of difference. In the British system, assessment is continuous and varied. Coursework, projects, oral presentations, class participation and exams are all taken into account, providing a more comprehensive picture of a student’s progress. Mistakes are seen as part of the learning process, and long-term development is valued.
In the Spanish system, although continuous assessment also exists, exams still carry greater weight. Written tests often play a decisive role in final grades, which can create higher academic pressure at certain points during the school year.
Curriculum flexibility and subject choice
A clear advantage of the British system is its flexibility in subject choice, particularly in the later stages. During A-Levels, students can select a small number of subjects aligned with their interests and university goals, allowing them to study these subjects in greater depth.
In the Spanish system, the curriculum is more rigid, with a broad set of compulsory subjects and more limited choice, even during Bachillerato. This provides a more general education but reduces opportunities for early specialisation.
Language and international environment
The British education system is delivered entirely in English, providing full language immersion. In addition, many British schools have highly international school communities, which encourages the development of intercultural skills and a global mindset from an early age.
The Spanish system, while it includes foreign language learning and bilingual programmes in many schools, does not generally offer the same level of linguistic immersion or cultural diversity.
University access and academic recognition
With regard to university access, both systems allow students to pursue higher education in Spain and abroad, although the pathways differ. The British system prepares students for international university entry, with strong emphasis on academic guidance and university application preparation.
The Spanish system is more focused on access to national universities through a centralised process, which provides clarity and consistency but may be less flexible for students wishing to study outside Spain.
Role of the teacher and student–teacher relationship
In the British system, the relationship between teachers and students is often closer and based on continuous tutoring. Teachers act as guides and mentors, supporting students’ academic and personal development. This relationship helps with early identification of difficulties and personalised support.
In the Spanish system, although tutoring exists, larger class sizes and the overall structure can make such personalised follow-up more challenging, particularly in high-demand public schools.
Which education system is better: the British or the Spanish?
There is no single answer to which education system is better, as both have strengths and cater to different needs. The British education system stands out for its practical approach, curriculum flexibility, English immersion and international outlook. The Spanish education system offers a more uniform education, strong cultural roots and a clear pathway to the national university system.
The choice between one system and the other depends on the student’s profile, long-term academic goals and family expectations. Analysing the differences between both systems is the first step towards making a well-informed decision about a child’s educational future.